FBT Reform: Government Confirms FBT Changes for Motor Vehicle Benefits Will Proceed
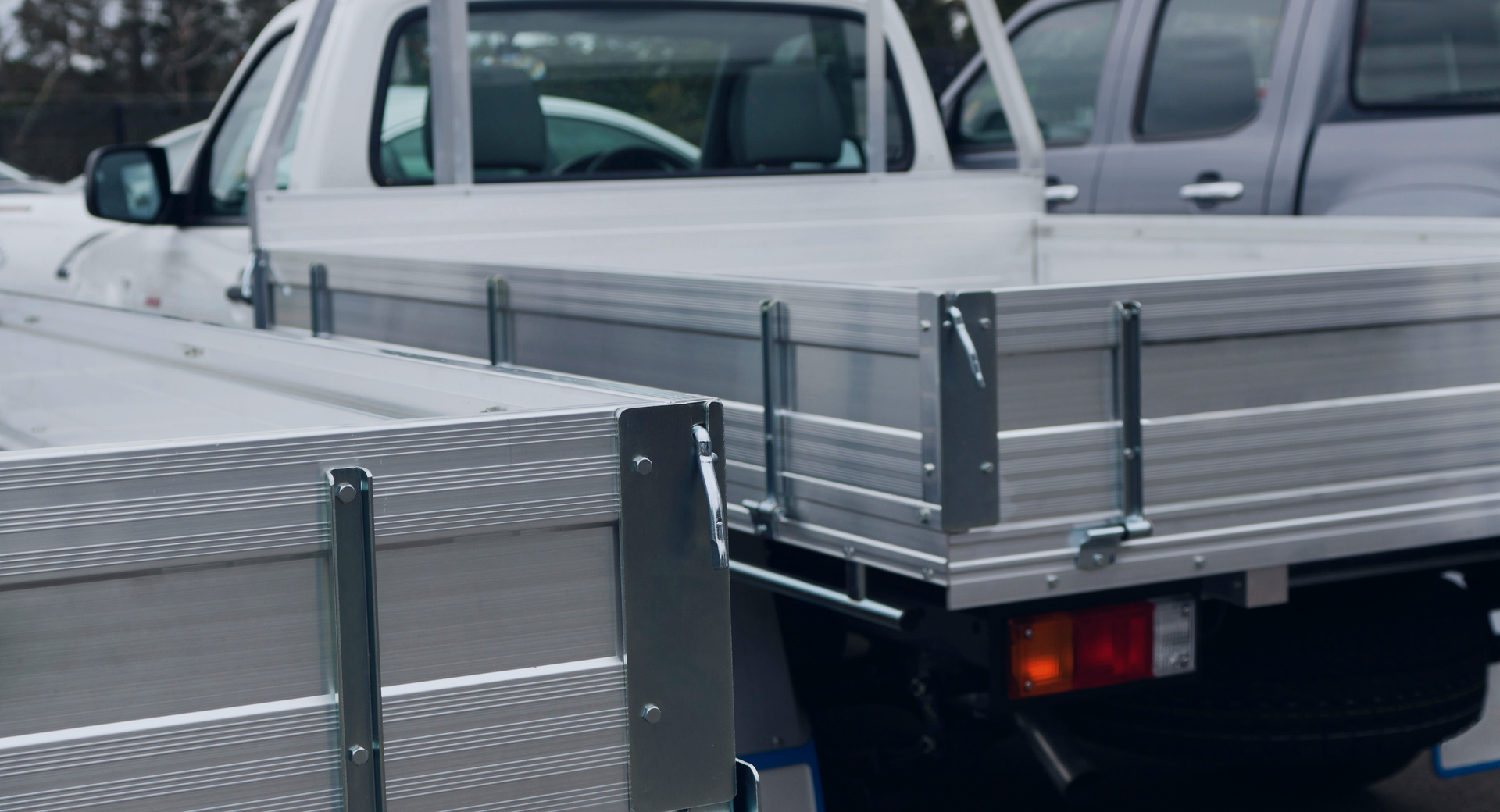
The end of the Work Related Vehicle FBT Exemption.
Last week’s Budget included in the fine print an intention to go ahead with the proposed FBT changes. Those proposals were announced recently in an Inland Revenue consultation document and signalled a significant overhaul of the FBT regime. The proposed changes, particularly around motor vehicles, represent a major shift in how FBT will be calculated and reported.
While the fine print is still pending, one headline change is already sending ripples through the business and accounting communities: the removal of the work-related vehicle exemption — a rule that has been extensively used (and loved) for decades.
Another significant issue raised by the proposals is the potentially punitive treatment of major shareholders of close companies with vehicles costing over $80,000.
What Was Announced?
The proposed changes represent a significant overhaul of a regime widely considered overdue for reform.
These proposals follow the 2022 FBT regulatory stewardship review, which found the current rules overly complicated, overly punitive in their anti-avoidance goals, and out of step with modern business practices, particularly when it comes to motor vehicles, a key focus of the reform.
A Key Casualty: The Work-Related Vehicle Exemption
The removal of the work-related vehicle exemption is potentially one of the most consequential aspects of the reform. Inland Revenue has noted widespread misconceptions about this exemption, often referred to as the “double cab Ute exemption”, which many assumed provided full FBT relief for such vehicles.
What remains unclear is how employers will now calculate FBT on the private use component of these vehicles. Will these vehicles now be treated as Category 1, with FBT applied to 100% of their value? The reforms aim to simplify, but this change may create new grey areas and complexities for employers.
That said, the proposals do hint at some relief: vehicles with genuinely minimal private use, such as pool vehicles, could be exempt or taxed under a concessionary approach, possibly removing many low-risk arrangements from the FBT net.
Recap: Key Motor Vehicle FBT Proposals
Among the most complex and widely criticised areas of the FBT regime is the treatment of motor vehicles. The current system taxes employers based on a vehicle’s availability for private use, not actual usage, requiring logbooks, declarations, and complex calculations.
Key proposed changes include:
1. Increased Vehicle Weight Threshold:
Reflecting the increased weight of modern vehicles, the FBT weight threshold for defining a car will rise from 3,500 kg to 4,500 kg.
2. Valuation Method Reforms:
- The option to use the tax book value to determine the value of a motor vehicle would be removed.
- Instead, the vehicle's FBT value would be calculated using external sources (e.g. data from the Automobile Association).
- These values would be re-calculated every four years to reflect depreciation and market conditions.
3. Optional Fuel Type-Based Valuation – Vehicle Categories with Fixed Rates:
New fringe benefit rates will apply depending on the fuel type of the vehicle, reflecting the vehicle’s environmental and economic characteristics, and calculated as a percentage of the vehicle’s cost price:
- Standard ICE vehicles would attract one rate
- Hybrids and electric vehicles may receive discounted rates to reflect lower operating costs.
4. Simplified Accounting for Private Use:
The requirement to maintain logbooks to track days when a vehicle is unavailable for private use would be removed. This would instead be captured during the vehicle's four-year valuation recalculation cycle.
5. Usage-Based FBT Categories:
A major change is the introduction of a new method to determine taxable value based on how the vehicle is used, rather than its type. The proposal categorises vehicle use into three groups.
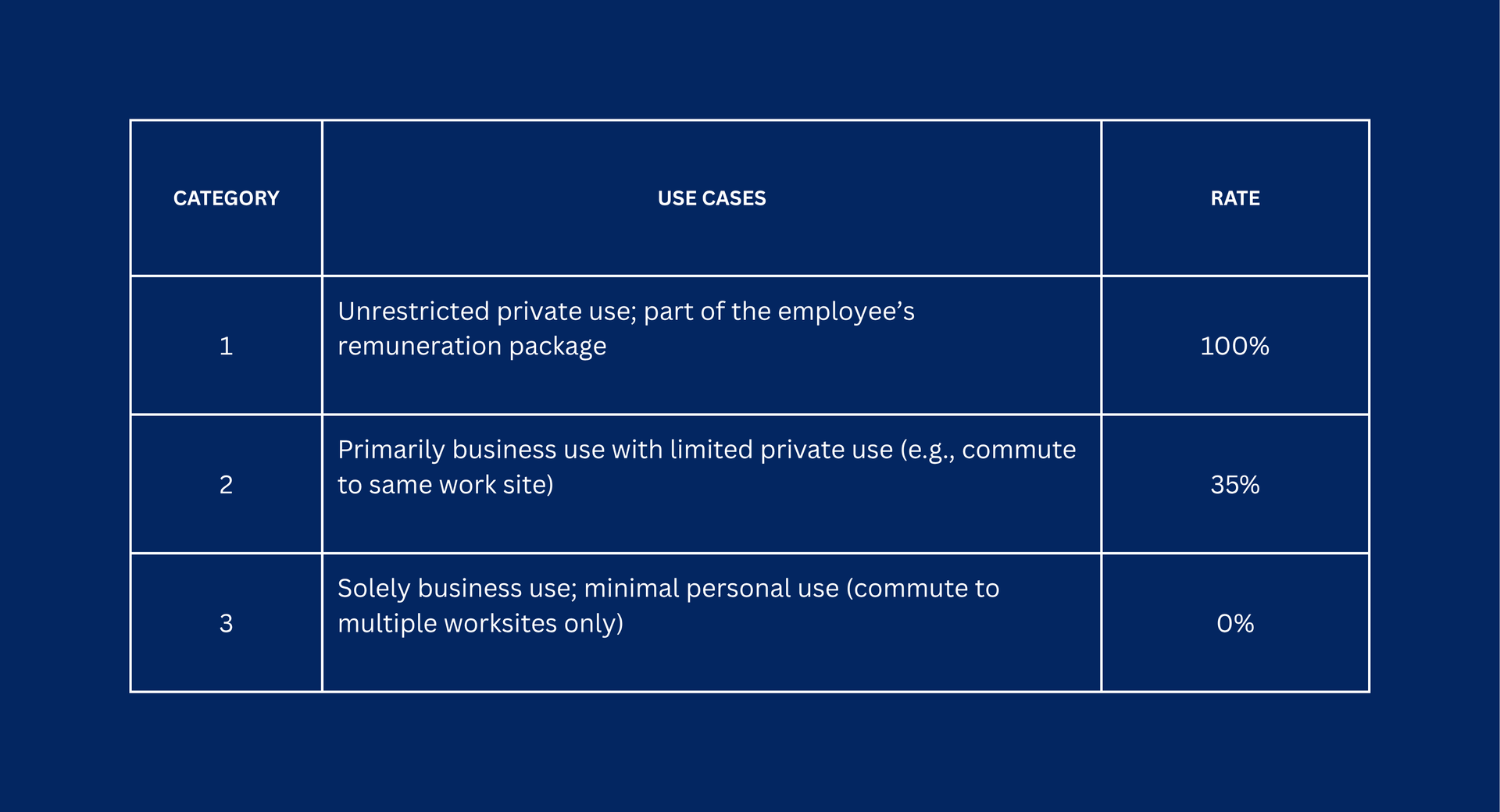
Category 2 and 3 vehicles may display employer branding, and Category 3 must have it.
For major shareholders of close companies, use of Category 2 or 3 would only be allowed for vehicles with a cost base under $80,000. Vehicles over $80,000 would have to use Category 1 – 100%.
6. New Concept – Incidental Travel:
The proposals introduce "incidental travel", defined as ad hoc, short-duration, non-remunerative, and irregular vehicle use, which may be ignored for FBT purposes, reducing unnecessary reporting for minor, one-off use cases.
What This Means for Accountants
The Government is moving forward with a landmark FBT reform, with motor vehicle benefits front and centre. The long-standing work-related vehicle exemption, particularly the commonly used double cab ute exemption, is set to be scrapped, marking a fundamental shift in how business vehicles are taxed.
Accountants will need to:
- Assist clients with the transition and possible revaluation of existing vehicles.
- Evaluate which method (prescribed or current) delivers the best tax outcome under the new rules.
- Review internal systems for data capture and reporting, especially if IR proceeds with proposed enhancements to digital reporting via myIR.
If you’d like to understand how these FBT changes may impact your business or clients, please
contact us.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is general in nature and does not constitute personalised tax advice. You should consult with a qualified tax adviser familiar with both US and NZ tax systems before making any decisions based on this content.